Sitemap
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there, there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Pages
Posts
SSH Tunneling
Published:
It seems that the VPN software we use at my university, a version of Forticlient, has some issues with route creation. Every time I set up Forticlient, all traffic gets redirected to the VPN gateway.
Intersection Dataset
Published:
Together with the colleagues of the INVETT group of Universidad de Alcalá, I am preparing a new multi-season dataset focused on the intersection detection issue. More details will be provided in the official website of the group.
Paper Accepted! Model Guided Road Intersection Classification
Published:
It is our pleasure to inform you that the paper identified above, for which you are listed as one of the authors, has been accepted as a contributed paper to be presented at the 2021 32nd IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV) (IV 2021), July 11-15, 2021, in Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan.
SSH Tunneling
Published:
From time to time, everyone has to deal with IT guys bizarre security habits. Among them, one of the most annoying are
OpenCV projectpoints function
Published:
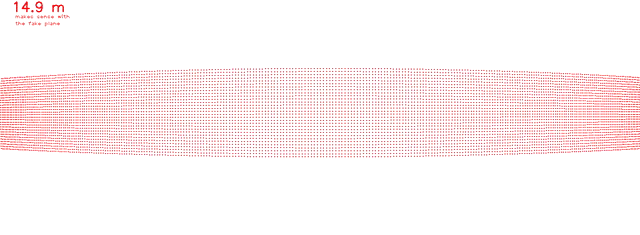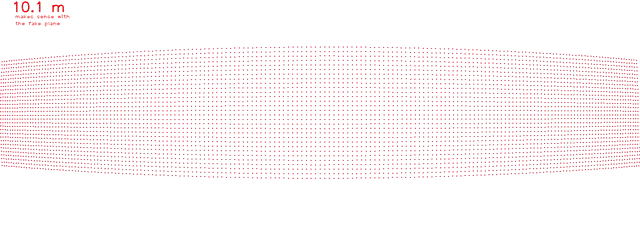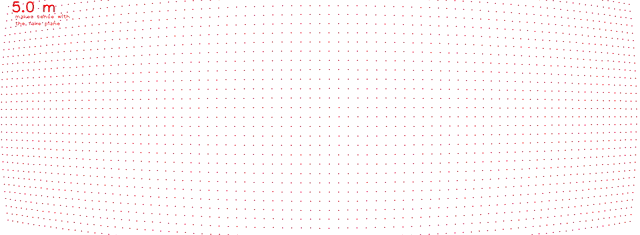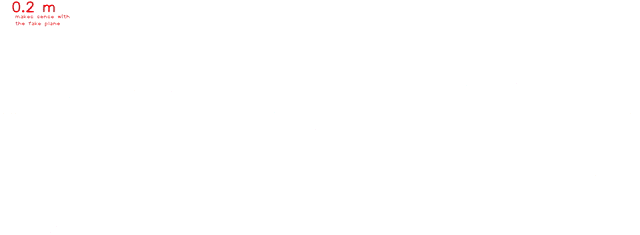
Hello World (Blog Launch)
Published:
This is the first post inside this blog. I will try to update this blog with some infos from general research activity, not strictly connected to a specific topic, just tech curiosities, news comments etc.
portfolio
Portfolio item number 1
Published:
Short description of portfolio item number 1
Portfolio item number 2
Published:
Short description of portfolio item number 2 
publications
6DoF Monte Carlo Localization in a 3D world with Laser Range Finders
Published in UNIMIB Internal Report, 2012
6DoF Monte Carlo Localization in a 3D world with Laser Range Finders
Recommended citation: Your Name, You. (2009). "Paper Title Number 1." Journal 1. 1(1).
Download Paper
ira_laser_tools: a ROS LaserScan manipulation toolbox
Published in arxiv, 2012
ira_laser_tools: a ROS LaserScan manipulation toolbox
Recommended citation: ballardini2014iralasertools
Download Paper
An effective 6DoF motion model for 3D-6DoF Monte Carlo Localization
Published in 4th Workshop on Planning, Perception and Navigation for Intelligent Vehicles, IROS, 2012, 2012
An effective 6DoF motion model for 3D-6DoF Monte Carlo Localization
Recommended citation: ballardini2012effective
Download Paper
A Framework for Outdoor Urban Environment Estimation
Published in 2015 IEEE 18th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015
A Framework for Outdoor Urban Environment Estimation
Recommended citation: ballardini2015
Download Paper
An Indoor Localization System for Telehomecare Applications
Published in IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, vol. 46, no. 10, pp. 1445-1455, Oct. 2016, 2015
An Indoor Localization System for Telehomecare Applications
Recommended citation: fontana2016
Download Paper
Leveraging the OSM building data to enhance the localization of an urban vehicle
Published in 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), 2016
Leveraging the OSM building data to enhance the localization of an urban vehicle
Recommended citation: ballardini2016
Download Paper
An online probabilistic road intersection detector
Published in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2017
An online probabilistic road intersection detector
Recommended citation: ballardini2017
Download Paper
Ego-lane estimation by modeling lanes and sensor failures
Published in 2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), 2017
Ego-lane estimation by modeling lanes and sensor failures
Recommended citation: ballardini2017b
Download Paper
Visual Localization at Intersections with Digital Maps
Published in 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2019
Visual Localization at Intersections with Digital Maps
Recommended citation: ballardini2019
Download Paper
CMRNet: Camera to LiDAR-Map Registration
Published in 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2019
CMRNet: Camera to LiDAR-Map Registration
Recommended citation: cattaneo2019
Download Paper
Vehicle ego-lane estimation with sensor failure modeling
Published in Preprint - ARXIV, 2020
Vehicle ego-lane estimation with sensor failure modeling
Recommended citation: ballardini2020vehicle
Download Paper
Global visual localization in LiDAR-maps through shared 2D-3D embedding space
Published in 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2020
Global visual localization in LiDAR-maps through shared 2D-3D embedding space
Recommended citation: 9196859
Download Paper
A benchmark for point clouds registration algorithms
Published in arxiv, 2021
A benchmark for point clouds registration algorithms
Recommended citation: FONTANA2021103734
Download Paper
Model Guided Road Intersection Classification
Published in arxiv, 2021
Model Guided Road Intersection Classification
Recommended citation: ballardini2021model
Download Paper
WiFiNet: WiFi-based indoor localisation using CNNs
Published in Expert Systems with Applications Volume 177, 1 September 2021, 114906, 2021
WiFiNet: WiFi-based indoor localisation using CNNsn
Recommended citation: HERNANDEZ2021114906
Download Paper
Fail-Aware LIDAR-Based Odometry for Autonomous Vehicles
Published in Special Issue "Intelligent Vehicles" - Sensors, 2021
Fail-Aware LIDAR-Based Odometry for Autonomous Vehicles
Recommended citation: s20154097
Download Paper
Vehicle Localization Using 3D Building Models and Point Cloud Matching
Published in Sensors, Volume 21, Number 16, 2021
Vehicle Localization Using 3D Building Models and Point Cloud Matching
Recommended citation: s21165356
Download Paper
CAPformer: Pedestrian Crossing Action Prediction Using Transformer
Published in Sensors, Volume 21, Number 17, 2021
CAPformer: Pedestrian Crossing Action Prediction Using Transformer
Recommended citation: s21175694
Download Paper
Urban Intersection Classification: A Comparative Analysis
Published in Sensors, Volume 21, Number 18, 2021
Urban Intersection Classification: A Comparative Analysis
Paper Title Number 4
Published in GitHub Journal of Bugs, 2024
This paper is about fixing template issue #693.
Recommended citation: Your Name, You. (2024). "Paper Title Number 3." GitHub Journal of Bugs. 1(3).
Download Paper
talks
ROS Introduction @ Linux Day Milano
Published:
Together with Pietro Colombo, I made a short presentation about ROS (in italian) Presentazione ROS Linux Day Milano 2018 and the history of autonomous driving cars Autonomous Road Vehicles History and Current Developments Powerpoint Presentation
Know where you are, drive where you want
Published:
After approximately one century from the first attempts to create automated driving cars, the recent progress in the context of Intelligent Transportation Systems allows us to consider the autonomous driving cars just a matter of time. From automated driving systems like on-demand next-generation taxis to privately owned self-driving cars, an appropiate awareness of the surrounding environment is a common need to achieve safety, for both drivers and road users. This presentations seeks to provide a basic understanding of one of the key elements in the process of achieving this self-consciusness, presenting the current advances in the field of vehicle localization. We will see together the major challenges and the different approaches both industries and academies are investigating to enable robotize-cars to drive safely in a real world shared with human drivers.
teaching
Computer Architecture (Architettura modulo Elaboratori)
Undergraduate course, Università degli Studi di Milano - Bicocca , 2014
From 2013 to 2018 I worked as teaching-assistant for the course Computer Architectures.
Robotics and Computer Vision
Master course, Università degli Studi di Milano - Bicocca , 2014
From 2013 to 2018 I worked as teaching-assistant for the course Computer and Robot Vision, together with Prof. Domenico G. Sorrenti. For this course I prepared the material for the exam and the lectures for the robotics localization topics, including:
Vehiculos Inteligentes
Master course, Universidad de Alcala , 2026
During the academic year 2019-20 and 2020-21 I have been teaching in the Vehiculos Inteligentes course (Intelligent Vehicles) of the Máster Universitario en Ingeniería de Telecomunicación (Telecommunication Engineering Master Course).
C Programming Course - PROGRAMACIÓN (350009)
Undergraduate, Universidad de Alcala , 2026
I serve as collaborator for the lab part of the “C Programming Course” - PROGRAMACIÓN (350009).
Sistemas en Tiempo Real - Real Time Systems (590008)
Undergraduate, Universidad de Alcala , 2024 - 2025
El incremento en fiabilidad y velocidad de proceso de los ordenadores, junto con una disminución en su tamaño y precio, ha hecho que los encontremos en todos los ámbitos de nuestra vida, desde un teléfono móvil hasta el control del tráfico aéreo. Una de las áreas de expansión más rápida de la explotación de ordenadores es la relacionada con los sistemas empotrados y de tiempo real. Estas áreas necesitan procesar información con el objetivo de controlar procesos. Se ha estimado que más del 90 por ciento de la producción mundial de microprocesadores se utiliza en este tipo de sistemas. Estas aplicaciones plantean requisitos específicos para lo lenguajes de programación necesarios para programarlos, ya que tienen características diferentes de las aplicaciones de procesamiento de información tradicionales.
theses
3D slam for autonomous vehicle
Published:
Aim (starting from the work by Nicolò Vecchio)
See IRALAB website.
A laser device and its calibration for the 3D Mapping Ground Truth project
Published:
Embedded Systems Development with ARM
This thesis focuses on a calibration system for a LiDAR device.
3D Mapping Ground Truth
Published:
Embedded Systems Development with ARM
The aim of this project is to develop a system that allows the creation of three-dimensional mapping models for autonomous navigation of IRALAB’s robots. To achieve this goal, we started our work with a device composed by a LIDAR (Laser Imaging Detection and Ranging) system, mounted on a rotating platform; this is capable of generating 3D points sets, also called point clouds, in a reference frame in agreement with the platform used.
Road Layout Estimation - A probabilistic framework for autonomous driving Cars
Published:
Description of the work:
Use of car’s sensor measurements as well as car’s motion model for scene layout estimation; development of the software infrastructure; determination of appropriate detectors for the baseline road features, e.g., lane markings (horizontal road markings); customization of the framework to integrate these layout components, integration of the detectors for such components, training of these detectors if appropriate, extensive experimental activity.
3D Mapping with laser scanners
Published:
Embedded Systems Development with ARM
Performing automatic point cloud merging on the laser scanner SickLms 200 and performing odometry on Robosoft Robuter
A robotic mapping platform based on laser scanner
Published:
Aim
The work aims at integrating some existing software modules in order to build a single robotic mapping application based on a laser scanner, rotated by a mechanical turret about a vertical axis; the work includes the development of the graphical interface and the display of 3D results and this will be based on publicly available existing components. The application will be deployed on the iralab mapper robot. In a first version, the robot will be moved by hand to perform some preliminary mapping of some university areas. Afterwards, a joypad will be integrated so to make it possible to remotely control the robot; this task will also be performed exploing existing software modules. In addition, if the 4 wheels (2 traction and 2 castor) configuration of the robot will turn out to be unsuitable for the foreseen operations of the robot (mapping of urban outdoor environments), I’ll work out a mechanical modification to reduce the 2 castor wheel to 1, so to have a 3 wheeler (2 traction and 1 castor) platform. In the end, an extended experimental work will be performed with the remote version of the application and robot.
Leveraging the OSM building data in the Road Layout Estimation Framework
Published:
Description of the work:
In this project I will develop the detector systems for determining the presence of some static parts of the scene observed by a forward facing cameras mounted on a urban road vehicle. These developments will be integrated in the iralab Road Layout framework. In particular, I will focus on crossings and buildings.
A probabilistic intersection detector for the Road Layout Estimation Framework
Published:
Description of the work:
Detecting buildings in the surrounding of an urban vehicle and matching them to models available on map services is an emerging trend in robotics localization for urban vehicles. In this paper we present a novel technique that improves a previous work in this area by taking advantage of detected building fac¸ade positions and the correspondence with their 3D models available in OpenStreetMap (OSM). The proposed technique uses segmented point clouds produced using stereo images, processed by a Convolutional Neural Network. The point clouds of the fac¸ades are then matched against a reference point cloud, produced extruding the buildings’ outlines, as available on OSM. In order to produce a lane-level localization of the vehicle, the resulting information is then fed into our probabilistic framework, called Road Layout Estimation (RLE). We prove the effectiveness of this proposal testing it on sequences from the well-known KITTI dataset and comparing the results the respect to a basic RLE version without the proposed pipeline.
Analisi, progettazione e implementazione di un registratore e riproduttore di traiettorie per robot mobili
Published:
Descrizione della tesi
Obiettivo: sviluppo di un software che consenta ad una generica piattaforma robotica di muoversi autonomamente seguendo una traiettoria predefinita
USAD GUI: progettazione ed implementazione di una interfaccia grafica per veicolo a guida autonoma
Published:
Descrizione della tesi
USAD GUI: progettazione ed implementazione di una interfaccia grafica per veicolo a guida autonoma
Robust Odometry for the USAD vehicles
Published:
Aim
The goal of this work is to carry out a USAD (Urban Shuttles Autonomously Driven) vehicle of a system that produced robust odometry. To achieve robust odometry, more heterogeneous sensors are used, as using only one technology would be unreliable. During the development of the work we added the covariance matrix to IMU messages using the information on the manual technician, the odometric messages presented the same problem that we solved by creating a matlab model that calculates the matrix covariance. The node communicating with the IMUs and posting messages had both issues in the frequency of message publishing and the time indicated in the message was incorrect. Both issues have solved them. We also made 3D and printed media for IMU.
Implementation of a motion planning algorithm for the Ackermann kinematics USAD vehicle
Published:
Descrizione della tesi
Lo scopo di questo lavoro è l’implementazione dell’algoritmo di pianificazione e controllo del moto per un veicolo a cinematica Ackerman. L’algoritmo è stato implementato all’interno dello stack di navigazione del framework ROS come un nuovo modulo di pianificazione locale, partendo da un prototipo sviluppato in MATLAB secondo un approccio noto in letteratura (U. Schwesinger, M. Rufli, P. Furgale, R. Siegwart - “A Sampling-Based Partial Motion Planning Framework for System-Compliant Navigation along a Reference Path”). La pianificazione del moto avviene basandosi su un percorso calcolato in precedenza da un altro modulo dello stack di navigazione, che si occupa della pianificazione globale.
Implementation of a global planner operating with OSM for the USAD vehicle
Published:
Aim
Currently the global planner of the IRALAB’s autonomous driven vehicle operates on image format maps (.png file). In these maps is represented the area where you want the vehicle to carry out the global motion planning. The stage activity will be focused on changing the global planner in order to operate with “openstreetmap” (https://www.openstreetmap.org/) so that the output would be a map on which it can then complete the global planning movement. The framework used will be ROS, changes to the navigation system will be done using C ++, all in Linux environment. It will be necessary to test the work that will be done directly on the vehicle, as the goal is to put the vehicle in the street.
Evaluation / Experimentation of mapping and localization systems in the university campus
Published:
Aim
The work involves an initial part that consists of mapping roads between the U9 and the U14 buildings, collecting and analyzing the data provided by the LIDAR sensors mounted onboard the vehicle. The acquired data will then be processed using open source software available on the ROS.org platform to create a true two-dimensional map of the explored environment needed for autonomous navigation. This activity is aimed at analyzing the current state of the system boundaries, designed to be used on areas not overly extensive. The possibility of making a modification to the existing software architecture will be evaluated to allow real-time navigation on maps, always related to the current position, via dynamic loading of maps of manageable dimensions. There is therefore an extensive testing phase on the autonomous machine of the IRALAB laboratory. As regards the training objectives, the student is expected to acquire the ability to understand the functioning of the ROS mapping (gmapping) and localization (amcl) stack as well as the operation of the framework itself; Moreover, any programming activity will take place in C ++, relying on the same framework and therefore it is expected that the student will also reach a discreet familiarity with this language.
Curb detection in urban environments using LiDAR pointclouds
Published:
Aim
Integration and implementation of a simple curb detection algorithm within the ROS navigation stack. The aim was to implement and integrate an algorithm in the vehicle’s local planner which allow to perform distance checks with reference to the roadway limits to ensure that the vehicle, in addition to follow a path set by the global planner, could be able to move in relationship with its position within the surrounding environment. The work and the analysis of the data acquired by the vehicle were processed using the ROS framework within Linux environment and the algorithm implementation was done in C++. Tests were carried out both in simulation and on the vehicle to verify the effective “operation” of the implemented work.
Integration in the navigation stack of the USAD vehicle of a vision-based tool for lane detection
Published:
Aim
The project involves the analysis of a detection algorithm for horizontal signage, in particular the lane detection. The aim is to create the limit zones beyond which the transit of a USAD cinema machine is not allowed, thus guaranteeing security in movement. A local planner of the autonomously guided vehicle is already present which decides instant by instant all the maneuvers that the kart must perform to maintain one trajectory; My work consist of integrating in local planner a control for not invading the opposite lane on the street. The framework used is ROS, the algorithm implementation is written in C ++ language, all in a Linux environment.
An extension of the ROS Navigation Stack for the management of moving obstacles
Published:
Aim
Integration and implementation of a dynamic obstacle detector in the ROS Navigation Stack. The project involves the development of an algorithm for the detection of dynamic obstacles commonly found in the urban environment. The developed software is integrated in the ROS navigation stack as a plugin that interfaces with the local planer and it’s able to represent static and dynamic obstacle on a 2D map.
A pedestrian detection module for the USAD vehicle
Published:
Descrizione della tesi
Il progetto consiste in un primo momento nel testare alcune reti neurali al fine di scegliere la migliore per rilevare ostacoli dinamici che intersecano la traiettoria del cart. Le reti neurali lavoreranno sulle rilevazioni ottenute da 3 telecamere montate sul veicolo a guida autonoma, due camere in bianco e nero sono in modalità stereo, mentre la camera a colori funziona singolarmente ed è montata tra le due precedenti. Le camere andranno quindi montate e calibrate correttamente al fine di ottenere dei bag da usare per testare gli algoritmi di riconoscimento. Scelto l’algoritmo migliore per le nostre necessità si procederà analizzando l’output ottenuto da esso per ricavarne informazioni relative al numero, tipo, posizione e velocità degli ostacoli presenti nell’ambiente. Queste informazioni saranno poi inviate al sistema in grado di gestirle e prendere decisioni sui movimenti del cart.
Construction of the physical support structure for a Velodyne 16P and testing of its functionalities
Published:
Descrizione della tesi
See IRALAB website.
Evaluation and experimentation of mapping and localization systems in the university campus
Published:
Aim (starting from the work by Nicolò Vecchio)
The involves an initial part that consists of mapping roads between the U9 and the U14 buildings, collecting and analyzing the data provided by the LIDAR sensors mounted onboard the vehicle. The acquired data will then be processed using open source software available on the ROS.org platform to create a true two-dimensional map of the explored environment needed for autonomous navigation. This activity is aimed at analyzing the current state of the system boundaries, designed to be used on areas not overly extensive. The possibility of making a modification to the existing software architecture will be evaluated to allow real-time navigation on maps, always related to the current position, via dynamic loading of maps of manageable dimensions. There is therefore an extensive testing phase on the autonomous machine of the IRALAB laboratory. As regards the training objectives, the student is expected to acquire the ability to understand the functioning of the ROS mapping (gmapping) and localization (amcl) stack as well as the operation of the framework itself; Moreover, any programming activity will take place in C ++, relying on the same framework and therefore it is expected that the student will also reach a discreet familiarity with this language.
Façade segmentation from 3D PointClouds for vehicle localization using Openstreetmap
Published:
Aim (starting from the work by Nicolò Vecchio)
See IRALAB website.
Creación de un mapa digital 3D de zonas urbanas a gran escala empleando sensores LiDAR y GNSS
Published:
Description of the work:
El objetivo de este proyecto es la creación de una nube de puntos de la ciudad de Alcalá de Henares en la que se registrará la precisión del sistema GPS. Asimismo, se pondrán a prueba distintas técnicas de SLAM basadas en algoritmos “LOAM”, tales como LegoLOAM, capaces de generar mapas 3D. Para el desarrollo de este proyecto se empleará el framework ROS (Robot Operating System), se adquirirán los datos mediante un sensor LiDAR, una IMU y un GPS. Cabe destacar que el algoritmo para la creación del mapa no se ejecutará en tiempo real, sino que los datos obtenidos por los sensores se recopilarán en un bag para su posterior procesamiento. Para determinar cual de los algoritmos es mejor se ha calculado el error medio de la trayectoria respecto a los datos del GPS, previamente transformados a coordenadas UTM, y se ha representado mediante “plot”de matlab ambas trayectorias juntas. El que menor error cometa, es el mejor algoritmo. En conclusión, se busca crear un sistema que permita la localización y mapeo con capacidad de identificar objetos en la ciudad de Alcalá de Henares. Para lograrlo, se implementarán técnicas de SLAM y análisis de datos, utilizando ROS, sensores LiDAR y herramientas de visualización.
Estudio de ablación para un detector de intersecciones viales
Published:
Description of the work:
En este trabajo se ha llevado a cabo un estudio de ablación detallado para un detector de tipologías de intersecciones viales basado en redes neuronales, centrado en el análisis exhaustivo del procesamiento de los datos de entrada, incluyendo transformaciones como rotaciones, traslaciones y variaciones en la resolución de las imágenes. A través de diversos experimentos, se han evaluado cuidadosamente las ventajas y desventajas que ofrece cada una de estas transformaciones, así como el impacto en el rendimiento de los modelos previamente definidos. Además, se proponen y discuten posibles mejoras y futuras direcciones para optimizar el estudio.
Geoestadística y Sistema de Información Geográfica para realizar predicciones y análisis de datos espaciales
Published:
Description of the work:
El trabajo consiste en la implementación de un Sistema de Información Geográfica para la predicción de precipitación mensual (mm de lluvia) en ubicaciones específicas a partir de los valores de las ubicaciones cercanas aplicando técnicas de geoestadística y diferentes métodos de interpolación espacial. La visualización de las predicciones se hará en un software de Sistema de Información Geográfica para presentar los resultados en mapas y gráficos que ayuden a visualizar los hallazgos de manera clara y comprensible para poder tomar decisiones.
Calibración y Validación de Sistemas de Visión Computacional para Aplicaciones con LiDAR y Cámaras
Published:
Visión Computacional / Redes Neuronales Profundas
Calibración y Validación de Sistemas de Visión Computacional para Aplicaciones con LiDAR y Cámaras
HUMANAV: Navegación Semántica Humanizada para Conducción Autónoma usando Representación del Conocimiento y Modelos de Lenguaje
Published:
HUMANAV: Navegación Semántica Humanizada para Conducción Autónoma usando Representación del Conocimiento y Modelos de Lenguaje
Probabilistic Camera-to-LiDAR Map Registration for Autonomous Vehicle Localization
Published:
<!– This project aims to enhance a deep-learning based system capable of localizing a vehicle inside a LiDAR map using images captured by onboard cameras. The latter is a well-established method first introduced by Daniele Cattaneo in the paper CMRNet: Camera to LiDAR-Map Registration and further expanded in the subsequent papers by Daniele. The systems hinges on the capability of deep-neural-netoworks to find a correspondences between the points of an existing map made with a LiDAR sensor and the correspondent pixels on the camera image. This matching is completely done by the neural-network acting like a black box, with no information about the reliability of the matching.
Evaluación de un Sistema de Detección de Intenciones de Peatones usando técnicas de Machine Learning
Published:
Redes Neuronales en Grafos / Knowledge Graphs (KG) / Knowledge Graph Embeddings (KGE)
Evaluación de un Sistema de Detección de Intenciones de Peatones usando Machine Learning
Sistema de Escaneo y Notificación de Trabajadores en Infraestructuras sin Necesidad de Etiquetas ni Localizadores (SENTINEL)
Published:
Sistemas en Tiempo Real - Sistemas Embebidos
Sistema de Escaneo y Notificación de Trabajadores en Infraestructuras sin Necesidad de Etiquetas ni Localizadores (SENTINEL)
Sistema de Monitorización Emocional del Conductor mediante Detección de Pulsación y Respiración por Radar
Published:
Sistemas en Tiempo Real - Sistemas Embebidos
Sistema de Monitorización Emocional del Conductor mediante Detección de Pulsación y Respiración por Radar
Sistema Predictivo de Colisiones para Asistencia en la Conducción mediante Radar y Microcontrolador
Published:
Sistemas en Tiempo Real - Sistemas Embebidos
Sistema Predictivo de Colisiones para Asistencia en la Conducción mediante Radar y Microcontrolador
Estimación de intenciones de cruce mediante modelos basados en grafos y datos de cámaras de tráfico globales
Published:
